TAX Offences And Penalties
Is income tax a “cost of doing business ?”
Many business entrepreneurs tend to agree that income tax is indeed a cost of doing business which would eventually affect their profit for dividend purpose. However, from the academic point of view, income tax is not a cost or overheads of a business! We leave that to the readers to decide.
Offences And Penalties
This part aims to highlight some of the offences and penalties under the Income Tax Act 1967 where many taxpayers are not aware of :-
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
OFFENCE | PENALTY |
|
|
Fail to pay the estimated tax installment on the due date |
The unpaid amount will be increased by 10% without any notice being served – Sec 107C(9) |
|
|
Failure to furnish a return –Section 77(1), 77(3) & 77A(1) | RM200 to RM20,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 112(1) |
|
|
Failure to give notice of chargeability –Section 77(3) | Where no prosecution, a penalty of up to 3 times the amount of tax – Section 112(3) |
| Incorrect return and/or incorrect information regarding income or chargeability | i) RM1,000 to RM10,000 fine together with a penalty of up to 200% of the amount of tax under charged – Section 113(1) ii) Where no prosecution, a penalty equal to the amount of tax undercharged – Section 113(2) | |
| Wilful evasion | RM1,000 to RM20,000 fine or 3 years’ imprisonment or both ; plus a special penalty of 3 times of the amount of undercharged – Section 114 | |
| Advise and/or assist (without reasonable care) others to under declare their taxes | RM2,000 to RM20,000 fine or 3 years’ imprisonment or both – Section 114(1A) | |
| Leaving Malaysia without payment of tax | RM200 to RM20,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both – Section 115(1) | |
| Obstruction of tax officers during their course of duties | RM1,000 to RM10,000 fine or 1-year imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 116 | |
| Businessmen failed to keep records as required under Section 82 | RM300 to RM10,000 fine or 1-year imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 119A | |
| Failure of an employer to furnish a return of his employees – Section 83(1) | RM200 to RM20,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 120(1)(b) | |
| Failure of an employer to give notice to IRB on commencement or cessation of work of employee – Section 83(2) and 83(3). Such notification however, may be exempted if the employee’s salary is deducted under Schedular Tax Deductions [STD] or below the minimum income for STD. | RM200 to RM2,0000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 120(1)(c) | |
| Failure of an employer to give notice to IRB on employee leaving Malaysia for more than 3 months – Section 83(3). | RM200 to RM2,0000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 120(1)(c) | |
| Contravention by taxpayers who fail to give notice for change of address – Section 89 | RM200 to RM20,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both upon conviction - Section 120(1)(d) | |
| Salary deducted and withheld upon the cessation of employee – Section 83(5) | RM200 to RM20,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 120(1)(e) | |
| Employers must remit the salary deducted upon the cessation of employee to IRB | RM200 to RM20,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both upon conviction – Section 120(1)(e) | |
| Failure to response to the IRB upon request of production of documents, any specific returns or attend to the IRB | RM200 to RM2,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both – Section 120(1)(a) | |
| Failure to produce statement of bank accounts as required by IRB – Section 79 | RM200 to RM2,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both – Section 120(1)(a) | |
| Failure to allow IRB officials to conduct inspection on lands, buildings and places and to all books and other documents | RM200 to RM2,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both – Section 120(1)(a) | |
| Fail to response to the IRB for information/particulars demanded | RM200 to RM2,000 fine or 6 months’ imprisonment or both – Section 120(1)(a) | |
| Fail to pay tax by non-business income individual by 30th April or permitted date after 30th Apr | Penalty of 10% will be imposed | |
| Fail to pay tax business income individual by 30th April or permitted date after 30th Apr | Penalty of 10% will be imposed | |
| Fail to pay tax by companies, LLPs, trust body or co-operative societies within 7 months from the end of their accounting period | Penalty of 10% will be imposed | |
| Fail to notify on the change of accounting period pursuant to Sections 21A(3A) & 112(3A) by companies, LLPs, trust bodies and co-operative societies | Where no prosecution, a penalty of up to 3 times the amount of tax – Section 112(3) | |
| Under estimate of tax payable when compare to actual tax payable to estimated or revised estimated tax payable where the under estimate amount is more than 30% | Penalty of 10% of the amount of that difference – Sec 107C(10) |
Example
Super Clean SB closes its account every 31st Aug. It has estimated and revised it tax payable for YA 2021 as follows :-
1. Filed CP204 – 31.07.2020 – RM12,000
2. Filed CP204A – 25.02.2021 – revised to RM8,000
3. Filed CP 204A – 22.06.2021 – revised to RM10,000
4. Actual tax payable – 25.03.2022 – RM14,500
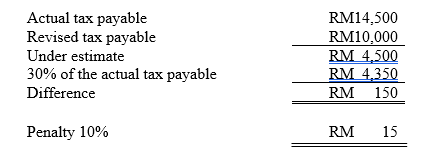
Conclusion
Taxpayers are strongly advised to adhere and comply in order to avoid the penalties as stated above, which may cause unnecessary cash outflow. Indeed, having the monthly unaudited accounts or managements accounts for the review of performance will not only help any business perform better but will ensure tax submission on time too!